
Grass Carp can disrupt the balance of aquatic life in lakes/rivers, alter nutrient cycles due to their aggressive eating behaviour, and reproduce rapidly. Additionally, Grass Carp have no predators in North America once they reach a certain size. Consequently, Grass Carp can increase competition and crowd out native fish species, including fish that are important for commercial and/or recreational fishing.
In 2019, Fisheries and Oceans Canada published a socio-economic risk assessment on the presence of Grass Carp in the Great Lakes Basin. This report provides critical information on impacts to our economy and society that could result if Grass Carp were to establish and spread. Information presented on this webpage summarizes some of the key findings from the report.
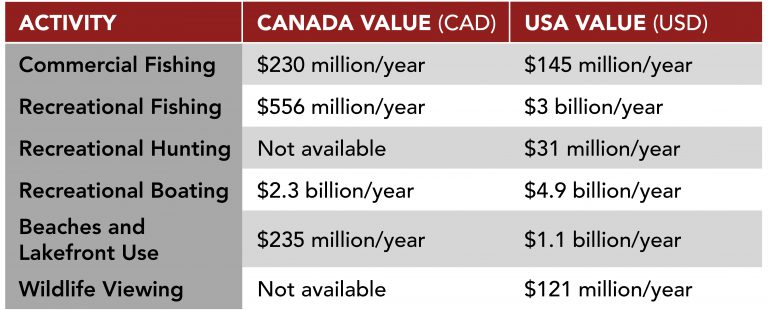
Baseline Values of Impacted Activities around the Great Lakes Basin
The Socio-Economic Risk Assessment of the Presence of Grass Carp in the Great Lakes Basin estimates economic values for various activities occurring in and around the Great Lakes Basin that may be impacted by Grass Carp. Baseline values were determined for commercial fishing, recreational fishing, recreational boating, hunting, beach and lakefront use and wildlife viewing. These baseline values were estimated using existing literature, where research focused on the expenditures made and consumer surplus for each activity. The baseline values of each activity can be found in Table 1.
Commercial Fishing
To assess the impacts of Grass Carp on commercial fishing, this study examined the ecological consequences on the native species which are fished commercially in the Great Lakes. The present estimated value of the commercial fishing industry is approximately $230 million (USD) per year in Canada and approximately $145 million (USD) per year in the U.S. The presence of Grass Carp would increase costs and decrease revenues for commercial harvesters and would have multiple impacts to commercial fishing, including:
- Reduction in food and habitat for commercially targeted fish populations, thereby reducing catches
- Reduction in quality of native fish species
- Increased operational costs of commercial fishing by causing commercial harvesters to travel further distances to catch fish, thereby decreasing profits
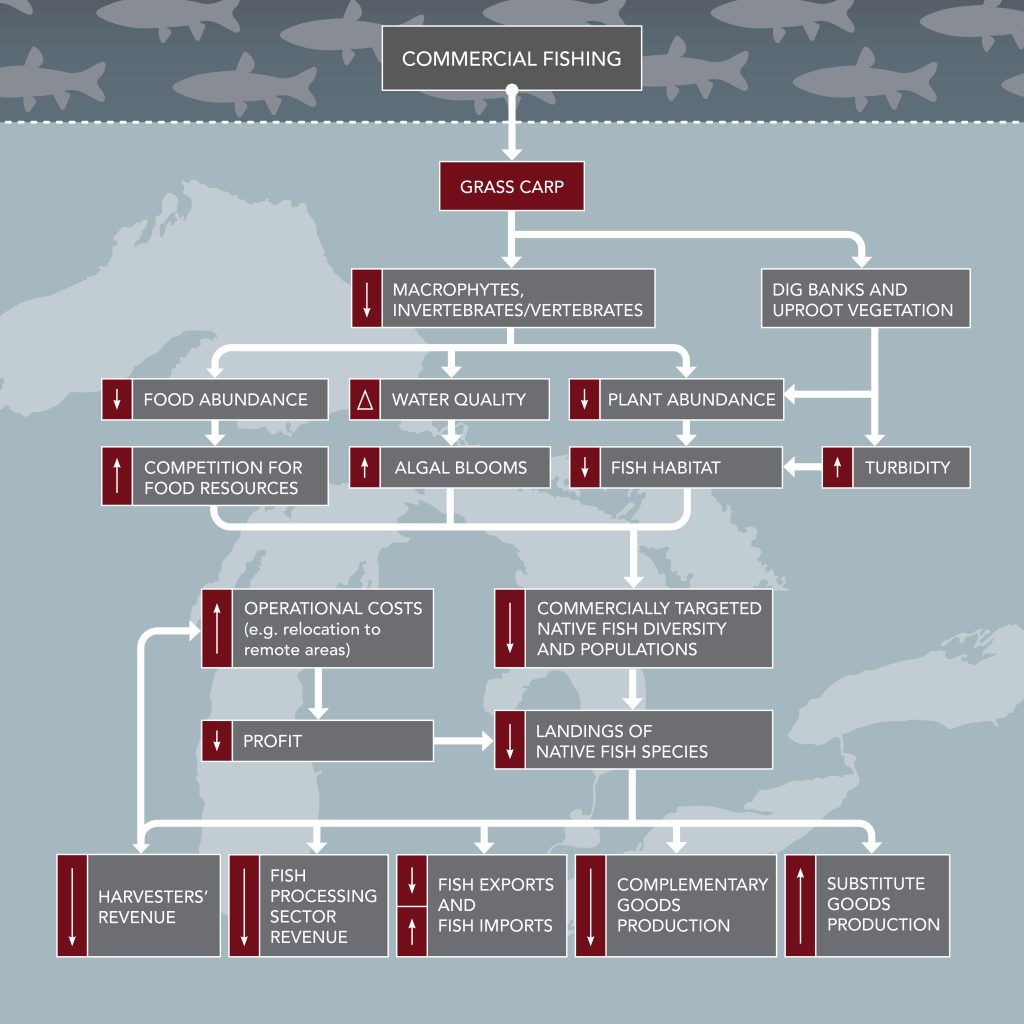
Major freshwater species groups internationally exported from the Canadian waters of the Great Lakes in 2016 were perch, whitefish, pickerel, trout, pike and smelt.
This study estimated that in the absence of additional prevention measures, the total estimated impact on the commercial fishing industry in 10 years would be $244 million in Canada and $102 million in the U.S.
Lake Erie would experience the highest impacts followed by Lake Michigan, Lake Huron and Lake Ontario. Impacts for Lake Superior are predicted to be negligible.
Recreational Fishing
The impacts on recreational fishing were determined by examining how anglers would be impacted. More specifically, the study looked at how the presence of Grass Carp would cause a reduction in the number of days anglers are out angling. The value of recreational angling is estimated to be worth approximately $556 million (USD) per year in Canada and $3 billion (USD) per year in the U.S. Grass Carp presence could have many impacts to recreational fishing, including:
- Reductions in native fish diversity and population sizes
- Decreased demand for fishing trips due to a decrease in quality of fishing days
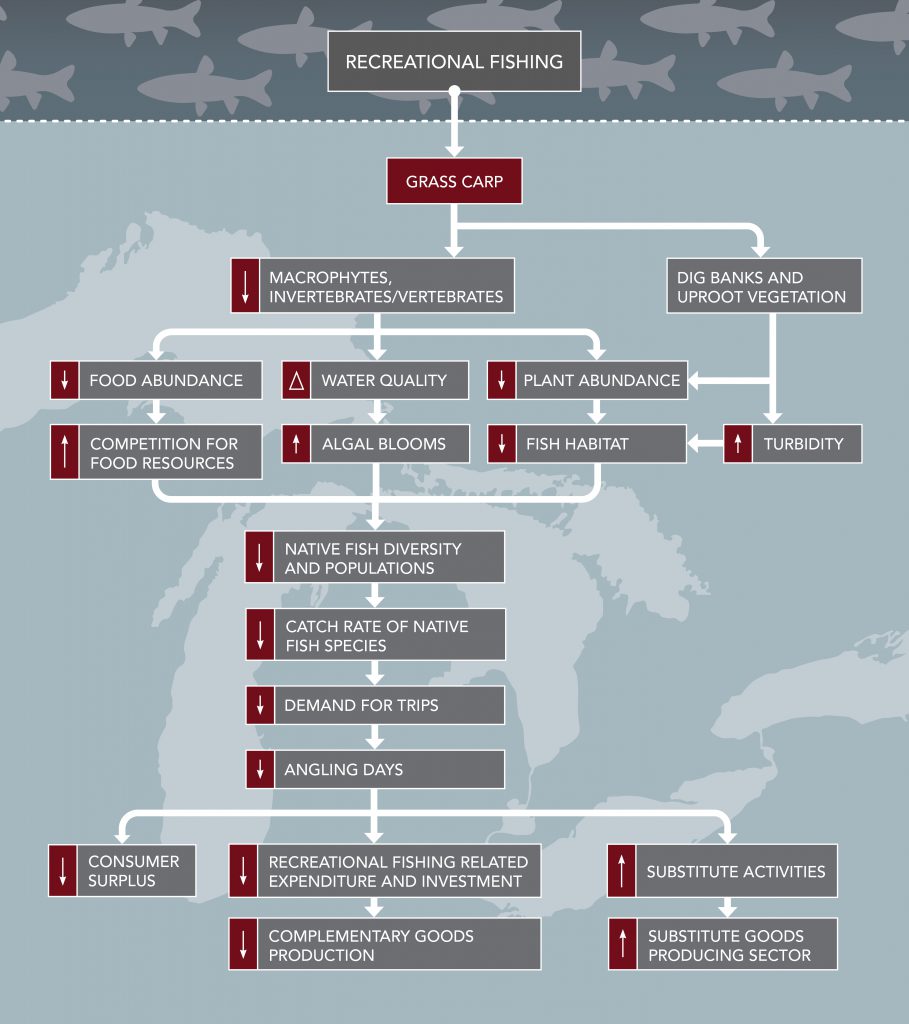
This study estimated that in the absence of additional prevention measures, in 10 years the damages to recreational fishing activities would be approximately $345 million (USD) in Canada and $2.4 billion (USD) in the U.S.
Lake Erie would experience the highest impacts followed by Lake Michigan, Lake Huron and Lake Ontario. Impacts for Lake Superior are predicted to be negligible.
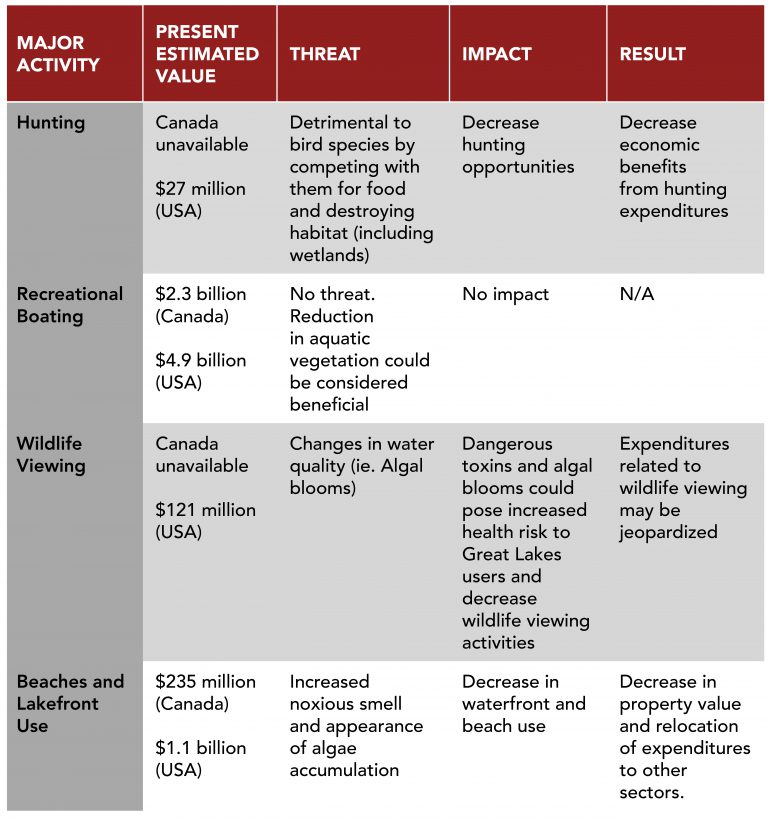
Impacts to Other Recreational Activities
Grass Carp presence could have negative impacts on other recreational activities in the Great Lakes region including hunting, boating, waterfront use and wildlife viewing. The results of the potential impacts to these activities are summarized in the table below.
Cultural and Social Impacts
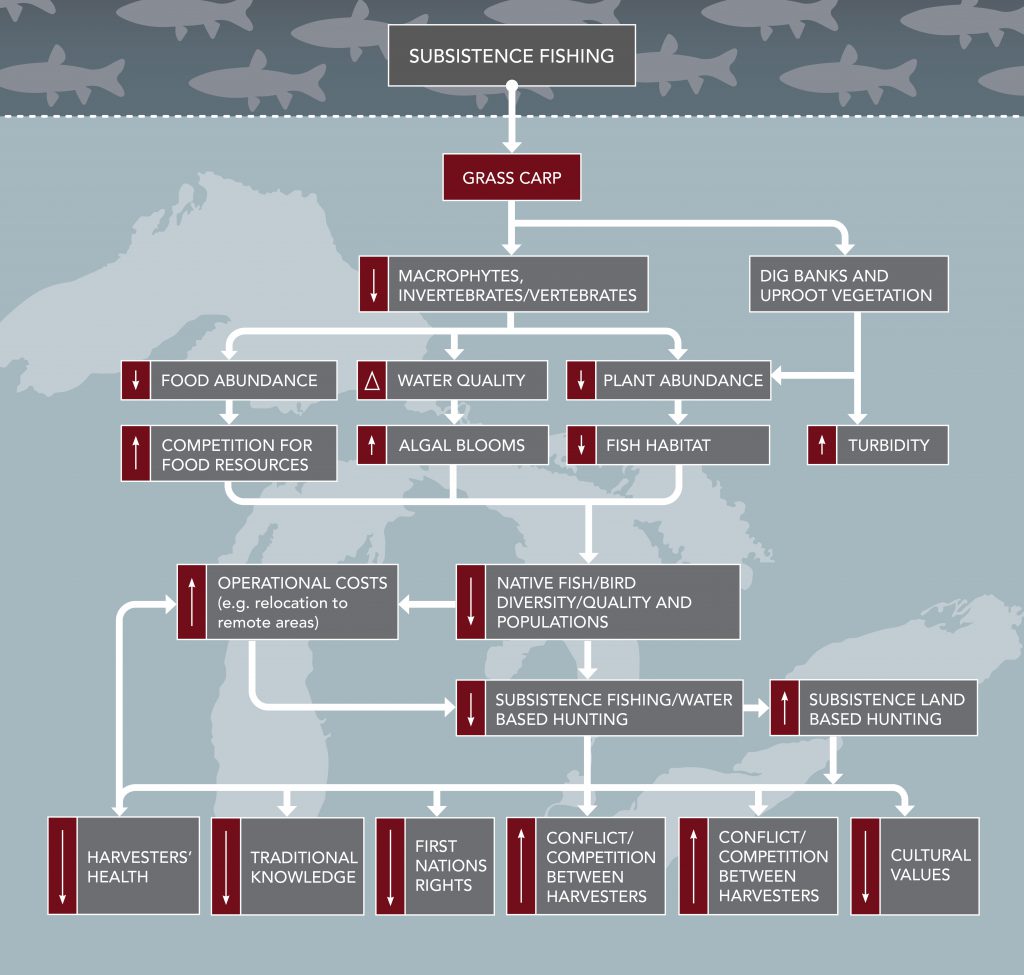
Cultural and social impacts are expected to occur if Grass Carp establish themselves in the Great Lakes. Grass Carp could damage the public image of the Great Lakes regionally, nationally and internationally; directly affect the well-being of residents who live in close proximity to the Great Lakes; cause potential damage to subsistence harvesters of native species; and reduce the social, cultural and spiritual values of the lakes and lake-related activities.
The study also discussed how subsistence harvesters may be impacted by Grass Carp establishment. Some of these impacts include:
- Changes in the ecosystem could result in reduced biodiversity and food quality for subsistence harvesters; could also impact First Nations Rights
- Increased costs of harvesting due to travelling greater distances in order to gain access;
- Weakened traditional knowledge and observations, weakened inter-generational transfer of knowledge and culture, and changes in ways of life
- Loss or degradation of fishing and hunting may impact traditional diets and threaten food security and health of First nation communities/individuals
- May also encourage increased competition among subsistence harvesters and between subsistence harvesters and recreational anglers for fewer native fish species
- Grass Carp may consume wild rice (Zizania palustris), a plant that is of conservation, rehabilitation and cultural value to the Great Lakes
Conclusion
The Great Lakes provide numerous services and benefits to the residents of Canada and the U.S. This study estimates that if no preventive measures are taken, that Grass Carp establishment in the Great Lakes basin could have many serious socio-economic impacts. There is currently no evidence of an established population in Canadian waters and Fisheries and Oceans Canada is continuing to work with partners in Ontario and the U.S. to prevent their establishment and protect Canada’s economic and social values through proactive prevention and response.
Read the full socio-economic risk assessment here.
Fisheries and Oceans Canada. Hayder, S. 2019. Socio-Economic Risk Assessment of the Presence of Grass Carp in the Great Lakes Basin.